If you aren’t familiar with bitter melon, it’s time to change that. Typically grown in Asia, Africa and the Caribbean, melon is increasingly available in the U.S.
It’s one of those meals that is officially a fruit but is utilized more like a vegetable because of its crisp texture and salty, bitter flavor. Known by another name, bitter gourd, it is prized for its flavor and remarkable nutritional value.
Recent studies have revealed some intriguing evidence that bitter melon may help control blood sugar.
Here’s everything you need to know about bitter melons, whether you’re attempting to maintain stable blood sugar levels or simply want to expand your intake of fruits and vegetables.
Contents
What Is Bitter Melon?
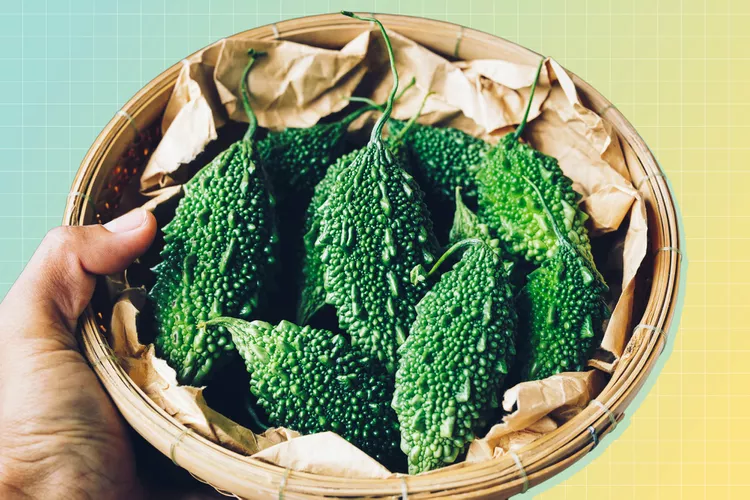

“Bitter-melon is technically a fruit of the gourd family,” according to Vandana Sheth, RDN, CDCES, FAND, a registered dietitian nutritionist located in Los Angeles and the author of My Indian Table: Quick & Tasty Vegetarian Recipes. It is also referred to as bitter gourd.
As a result, it belongs to the same family as other fruits and vegetables, including pumpkin, cucumbers, zucchini, and melon. Chinese and Indian bitter melon are the two primary types. Both have spherical, lengthy bodies with green skin and cucumber-like, pale, whitish meat. “The Chinese variety is long and light green with bumps, and the Indian variety is narrow and has a rough and spiky rind,” Sheth explains Discover the Power of Bitter-Melon: Can It Help You Balance Blood Sugar?.
The fruit is commonly used in Asia and the Middle East, and you’ll likely be able to purchase it at Asian stores and other specialized grocers here in the United States.
What Does Bitter Melon Taste Like?
In contrast to most melons, bitter-melon lacks sweetness and has a strong bitter flavor. As the fruit ripens, it actually becomes more bitter. Its white insides and green husk are both edible, and although bitter-melon can be eaten raw, many people prefer it cooked because the bitterness is lessened.
What Are Bitter Melon’s Nutrients?
According to the USDA, one cup of cooked bitter melon has the following nutritional value:
- Calories: 53
- Carbohydrate: 5.5 g
- Fiber: 2.5 g
- Total Sugar: 2.5 g
- Added Sugar: 0 g
- Protein: 1 g
- Fat: 3.5 g
- Saturated Fat: 1 g
- Sodium: 166 mg
Furthermore, one cup of bitter-melon has around half of the daily intake of vitamin C, making it a great source of the vitamin. In addition to having antioxidant qualities that help ward off harmful free radicals, vitamin C is a nutrient that is essential for the formation of collagen, which is required for wound healing and maintaining the springiness of skin, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH). According to a 2021 review published in Diabetes Care, there is also some evidence that vitamin C may help persons with type 2 diabetes manage their blood pressure and blood sugar. According to the NIH, bitter-melon also contains vitamin A, a fat-soluble vitamin crucial for immunological function.
A serving of bitter-melon also contains 2.5 grams of fiber, which stabilizes blood sugar and aids in digestion. According to Erin Palinski-Wade, RD, CDCES, a dietitian based in New Jersey and the author of the 2 Day Diabetes Diet, “Anyone looking to increase their overall fiber intake to benefit gut health, as well as those looking to add more volume and satiety to their meals, can benefit greatly from adding bitter-melon to their plate as a high-fiber, low-calorie food with a high level of the antioxidants vitamin A and C.”
Does Bitter Melon Help with Blood Sugar Management?
All high-fiber, low-sugar fruits and vegetables can help to keep blood sugar steady, because they provide valuable nutrients as well as fiber that slows the absorption of glucose into your bloodstream. Bitter-melon may be particularly good at keeping blood sugar stable. “The key nutrient in bitter-melon that may be beneficial for blood sugar management is a chemical called polypeptide-P that acts like insulin,” says Sheth.
So, what does that mean? “Bitter-melon appears to contain insulin-like properties that help your cells utilize glucose and transport it around your body, while also helping to promote insulin secretion,” explains Palinski-Wade. “Several small studies indicate it may be beneficial at reducing overall blood glucose levels and A1C in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
In addition to being used for generations to help control blood sugar, a 2022 review in Food Production, Processing, and Nutrition argues that a large number of research appear to support bitter-melon’s anti-diabetic properties, which means that it can help prevent or treat diabetes by stabilizing blood sugar.
Researchers administered bitter-melon extract to subjects for 12 weeks in a 2023 Food Science and Biotechnology study. After 12 weeks, the group that received the bitter-melon extract showed notable improvements in their blood glucose levels when compared to the placebo group.
How to Start Using Bitter Melon
Caraili (Sautéed Bitter Melon), a Trinidadian meal that counter balances its bitter flavor with salt and spice, is a good place to start if you’ve never cooked bitter-melon. In the winter months, you might try this Yeo Joo Ggori Tang (Oxtail & Bitter-Melon Soup), which is full of savory, sweet, and bitter flavors. Bitter-melon is also utilized as a soup ingredient.
The Bottom Line
The experiments that have been conducted are encouraging, but further research is required to ascertain whether and why bitter-melon appears to aid in blood sugar regulation. Pick up some bitter-melon and start cooking the next time you see it at your market or grocery store.